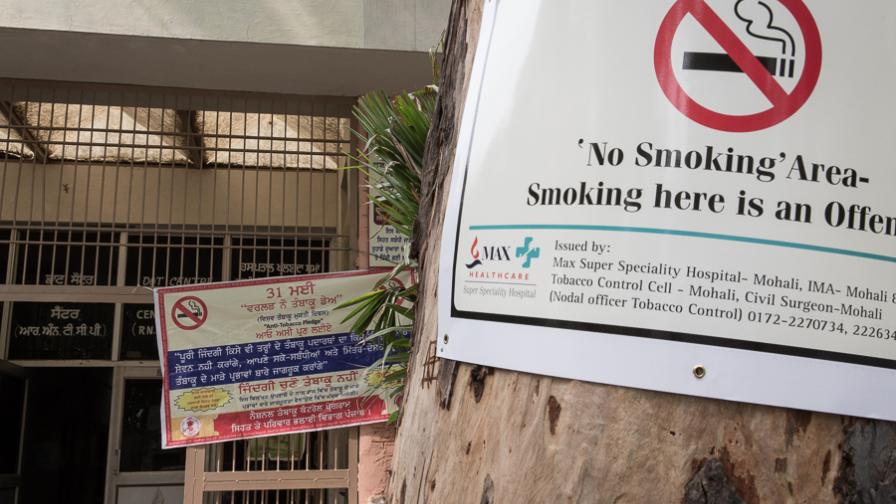
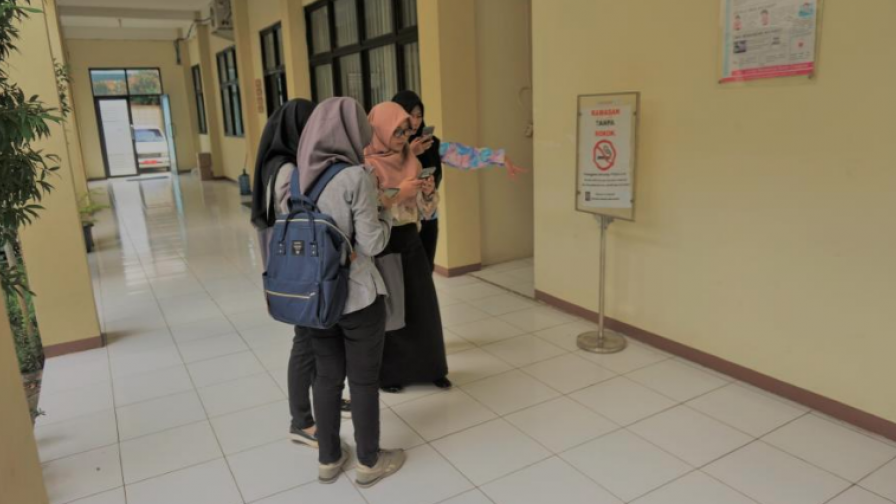
GOAL: Increased compliance with the tobacco control law leading to greater protection of the population.
With increased compliance with tobacco control laws there is greater protection of the population which ultimately reduces smoking prevalence, tobacco consumption, tobacco-related morbidity and mortality, and tobacco-related disparities.

The Johns Hopkins University School of Public Health is supporting the program by conducting pre- and post-compliance surveys in each city.
Baseline surveys have taken place in all countries and indicate a strong need for improved compliance.
Find results from the Compliance Surveys Below:
Implementation Areas
Legislation
Effective tobacco control laws are passed by a legislative body to protect the public from the harms of tobacco use.
Regulations
Issued by an executive authority or government regulatory agency, a regulation (or rule, order, ordinance or guideline) explains how to implement a specific law and its related penalties and sanctions.
Countering Industry Interference
Extreme vigilance is the only way to counter the tobacco industry’s attempts to interfere with and muddy public health policies.
Coordination and Planning
Multiple government agencies are frequently tasked with tobacco control law implementation and enforcement. Effective coordination and communication between them is key.
Stakeholder mobilization
Tobacco control law compliance depends on diverse stakeholders with both the capacity and commitment to effectively implement and enforce them.
Public communications
Public education campaigns enumerating the benefits of tobacco control legislation help build consensus and facilitate smooth implementation.
Enforcement Actions
Multiple agency coordination, stakeholder engagement with stakeholders, and strategy and planning activities are all critical components of enforcement.
Monitoring and Evaluation
A plan to assess progress and evaluate impact must precede implementation.